采用三次函数拟合了中国对虾“黄海1号”和野生群体F1代的生长曲线,并给出了两群体拟合生长曲线和各性状达到最大生长速度的月龄(拐点月龄)和体重及各形态性状长度。
表47 中国对虾“黄海1号”和野生群体F1代的体重模型参数

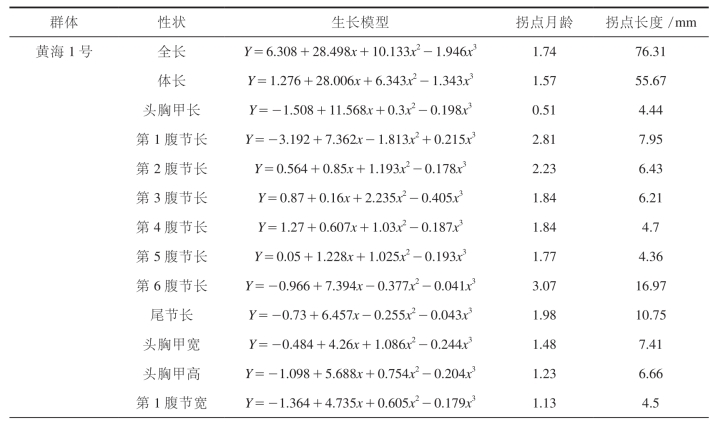
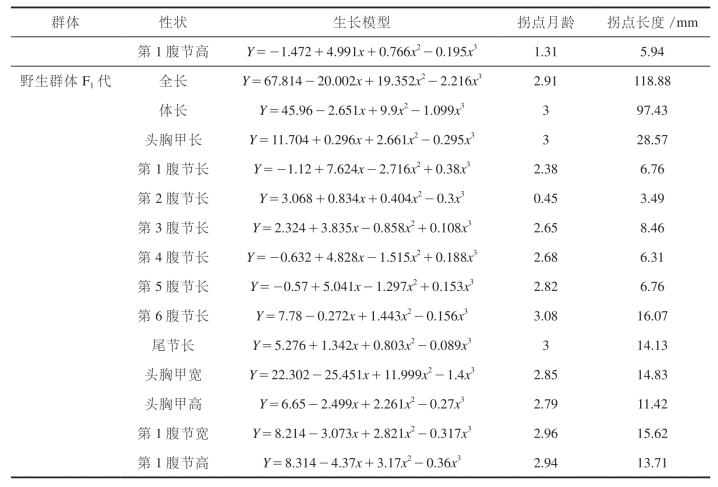
表48 中国对虾“黄海1号”和野生群体F1代各形态性状模型参数
续表
从表47可以看出,中国对虾“黄海1号”体重达到最大生长速度约在放苗后的3个月,即7~8月份之间。此时拐点体重为14.98 g,而野生群体F1代体重达到最大生长速度约在放苗后的4个月,与黄海1号相比,野生群体F1代的体重延缓了1个月左右,拐点体重为26.26 g。
中国对虾“黄海1号”的全长,体长,头胸甲长、宽、高,各腹节长,尾节长及第1腹节的宽和高等14个形态性状达到最大生长速度拐点月龄分布在0.51~3.07之间(表48)。其中头胸甲长达到最大生长速度最早,拐点月龄(头胸甲拐点长度)为0.51(4.44),腹节6、腹节1和腹节2达到最大生长速度最晚,拐点月龄分别为3.07(16.97)、2.81(7.95)和2.23(6.43)。其余各形态性状的拐点月龄分布在1.13~1.98之间,分布比较集中。各形态性状达到最大生长速度的顺序分别为:头胸甲长 . 第1腹节宽 . 头胸甲高 . 腹1高 . 头胸甲宽 . 体长 . 全长 . 腹节5长 . 腹节3和4长 . 尾节长 . 腹节2长 . 腹节1长 . 腹节6长。
中国对虾野生群体F1代各形态性状中,除腹节2的长度达到最大生长速度的拐点月龄(腹节2拐点长度)在0.45(3.49)以外,其他各形态性状的拐点月龄均分布在2.38~3.08之间。与中国对虾“黄海1号”相比,各形态性状生长延缓了1个月左右。野生群体F1代各形态性状达到最大生长速度的顺序分别为:腹节2长 . 腹节1 长>腹节3长 . 腹节4长 . 头胸甲高 . 腹节5长 . 头胸甲宽 . 全长 . 腹1高 . 腹1 宽 . 尾节长5 头胸甲长5 体长 . 腹节6长。另外,除第1和第2腹节长两个性状外,中国对虾“黄海1号”各形态性状达到最大生长速度的拐点月龄均比野生群体F1代的早。这说明经过10多年的选育,中国对虾“黄海1号”的生长规律发生一定程度的变化,体重和体长等形态性状较早地进入了快速生长时期,达到最大生长速度的时间较未选育的野生群体F1代提前了1个月左右。

图6 中国对虾“黄海1号”和野生群体F1代各形态性状拐点月龄分布
中国对虾主要产于我国黄渤海域,因其生长快、养殖周期短、经济效益高等优点而成为我国重要的海水养殖种类。但是,近年来随着养殖规模的不断扩大、养殖自身污染积累以及病原变异等问题的加剧,对虾养殖产业的可持续发展受到明显制约。中国对虾养殖业在1993年以后遭受白斑综合征病毒(WSSV)病的重创,对虾养殖生产严重滑坡,年产量长期在5万吨左右徘徊,所造成的经济损失高达上百亿元人民币。中国对虾的生长易受环境因素的影响,在整个生长过程中,各个时期的测定值总是在生长曲线上下波动,有时甚至远离正常曲线,从而影响生长性状的遗传参数和遗传进展的精确估计,且无法判别养殖过程中的饵料供应情况,所以建立中国对虾的生长模型,分析其生长规律,可为中国对虾的选择育种工作提供理论依据。
本研究采用4种曲线模型对中国对虾“黄海1号”和野生群体F1代的生长规律进行拟合,均得到了较好的拟合效果,其中以三次函数模型的拟合度最高,最能反映两群体在养殖过程中体重、全长、体长等各形态性状的生长规律。根据采用三次函数模型对两群体各性状估计的拐点月龄可以看出,中国对虾“黄海1号”的体重在放苗后2.87个月,即7月28日前后就达到最大的生长速度,拐点体重为14.98 g。而中国对虾野生群体F1代的拐点月龄为4.05,即8月30日左右才能达到最大生长速度,比中国对虾“黄海1号”发育迟缓了1个月左右,这与赵晓临等对辽宁、盘锦二界沟镇养殖场的池养中国对虾体重的拐点月龄提早15 d。分析其主要原因可能与人工选育有关,中国对虾“黄海1号”经过10多年的选育,在逐代选育过程中将生长缓慢、发育迟缓的个体淘汰掉,将生长快的基因在选育过程中进行“富集”,逐步提高中国对虾“黄海1号”的生长速度,使中国对虾“黄海1号”的生长速度加快,与未经选育的野生群体F1代相比,具有个体大、生长快等优良性状。胡品虎等(1995)研究了江苏省大丰县池养中国对虾的生长特性,体重达到最大生长速度的时间为8月7日,认为生长曲线拐点前的1个月及拐点后的1个半月均是池养对虾的主要增重阶段。
从其他形态性状包括全长、体长、头胸甲长、各腹节长等也可以看出,中国对虾“黄海1号”除第1和第2腹节长两性状达到最大生长速度迟缓于野生群体F1代外,其他12个形态性状的拐点月龄均小于野生群体F1代的拐点月龄,这与李朝霞等(2006)的研究结果较一致,说明了中国对虾“黄海1号”在选育过程中通过增加全长及腹节的长度来维持其优良的生长优势。中国对虾“黄海1号”与野生群体F1代的第6腹节长几乎同时达到最大生长速度,拐点月龄分别为3.07和3.08,但达到拐点月龄时的拐点长度分别为16.97mm和16.07mm,比野生群体F1代长近1mm,这从另一角度证实了中国对虾“黄海1号”在生长性状上的优势。
通过本研究的研究结果可以看出,中国对虾“黄海1号”各形态性状达到最大生长速度的时间不同,因此,在养殖过程中应该根据中国对虾“黄海1号”的生长曲线,在拐点月龄前后,加强投饵的种类和数量,提供丰富的营养供给,以保证中国对虾“黄海1号”的生长需要,以获得更好的养殖效果。
[1] 安丽,刘萍,李健,等 .“黄海1号”中国明对虾形态性状对体质量的影响效果分析[J] .中国水产科学,2008,15:779-786.
[2] 包振民,张全启,王海,等 .中国对虾三倍体的诱导研究—细胞松弛素B处理[J] .海洋学报,19.3.15(3):101-105.
[3] 蔡难儿,林峰,柯亚夫,等 .中国对虾人工诱导雌核发育的研究Ⅰ—四步诱导法[J] .海洋科学,1995,3:35-41.
[4] 常亚青,刘小林,相建海,等 .栉孔扇贝中国种群与日本种群杂交子一代的中期生长发育[J] .水产学报,20.3.27(3):193-199.
[5] 陈本难,蔡难儿,李光友 .中国对虾人工诱导雌核发育的研究—紫外线辐射对精子顶体反应和受精能力的影响[J] .海洋科学,1997,1:41-47.
[6] 陈刚,柴华金,林晓文 .罗氏沼虾体长和体重的一些遗传参数分析[J] .湛江水产学院学报,19.6.16(1):25-30.
[7] 陈来钊,王子臣 .温度对海湾扇贝与虾夷扇贝及其杂交受精、胚胎和早期幼体发育的影响[J] .大连水产学院学报,19.4.9(4):1-9.
[8] 陈逑,相建海,秦裕江,等 .海湾扇贝、栉孔扇贝和虾夷扇贝杂交育种可行性研究Ⅰ异种配子亲和性和杂种的早期发育[M] .青岛:青岛海洋大学出版社,1991.
[9] 陈永胜,姚雄志,谢大敬 .不同养殖密度下鲟鱼生长规律的研究[J] .水利渔业,20.4.24(5):43-44.
[10] 戴继勋,包振民,张全启,等 .60Co g射线诱导中国对虾雌核发育的观察[J] .青岛
海洋大学学报,19.3.23(4):151-154.
[11] 戴继勋,包振民,张全启 .中国对虾三倍体的诱发研究—温度休克[J] .遗传,19.3.15(5):15-18.
[12] 邓景耀 .对虾渔业生物学研究现状[J] .生命科学,19.8.10(4):191-196.
[13] 董世瑞,孔杰,万初坤,等 .中国对虾形态性状对体重影响的通径分析[J] .海洋水产研究,20.7.28(3):16-22.
[14] 高冬梅,李健,王清印 .养殖对虾新品种培育技术研究进展[J] .中国水产科学,2002,9:375-378.
[15] 耿绪云,王雪惠,孙金生,等 .中华绒螯蟹一龄幼蟹外部形态性状对体重的影响效果分析[J] .海洋与湖沼,20.7.38(1):49-54.
[16] 何玉英,李健,刘萍,等 .中国对虾“黄海1号”与野生群体F1代生长发育规律比较[J] .中国海洋大学:自然科学版,2009,39:413-420.
[17] 何玉英,李健,刘萍,等 .中国对虾养殖群体生长和抗逆性状杂交优势和生长相关分析[J] .中国海洋大学学报(自然科学版),20.1.41(增刊):154-160.
[18] 何玉英,刘萍,李健,等 .中国对虾人工选育群体第一代和第六代遗传结构分析[J] .中国水产科学,20.4.11(6):572-575.
[19] 何玉英,刘萍,李健,等 .中国对虾与生长性状相关SCAR标记的筛选[J] .海洋与湖沼,20.7.38(1):54-60.
[20] 何玉英,王清印,谭乐义,等 .中国对虾生长性状的遗传力和遗传相关估计[J] .安徽农业科学,2011,(17):10499-10502.
[21] 胡品虎,唐天德,沈涛 .中国对虾在池塘中生长特性的研究[J] .水产养殖,1995,4.18.21 .
[22] 黄付友,何玉英,李健,等 .“黄海1号”中国对虾体长遗传力的估计[J] .中国海洋大学学报,20.8.38(2):269-274.
[23] 姜勋平,刘桂琼,杨利国,等 .海门山羊生长规律及其遗传分析[J] .南京农业大学学报,20.1.24(1):69-72.
[24] 敬艳辉,邢留伟 .通径分析及其应用[J] .统计教育,2006,2:24-26.
[25] 兰进好,张宝石,周鸿飞 .作物杂种优势遗传基础研究进展[J] .中国科学通报,20.5.21(1):114-119.
[26] 李朝霞,李健,王清印,等 .中国对虾“黄海1号”选育群体与野生群体F1代的形态特征比较[J] .中国水产科学,20.6.13(3):384.3.8 .
[27] 李健,高天翔,柳广东,等 .中国对虾人工选育群体的同工酶分析[J] .海洋水产研究,20.3.24(2):1-8.
[28] 李健,刘萍,何玉英,等 .中国对虾快速生长新品种“黄海1号”的人工选育[J] .水产学报,20.5.29(1):1-5.
[29] 李健,牟乃海,孙修涛,等 .无特定病原中国对虾种群选育的研究[J] .海洋科学,20.0.25(12):30-33.
[30] 李健,孙修涛,高成年,等 .养殖中国对虾育苗效果观察[J] .海洋科学,1992:18-22.
[31] 李健,王清印 .中国对虾高健康养殖品种选育的初步研究[J] .中山大学学报,20.0.39(增刊):86-90.
[32] 李明爽,傅洪拓,龚永生,等 .杂种优势预测研究进展[J] .中国农学通报,2008,24(1):117-122.
[33] 李思发,李晨虹,李家乐 .尼罗罗非鱼品系间形态差异分析[J] .动物学报,1998,44(4):450-457.
[34] 李素红,张天时,孟宪红,等 .中国对虾杂交优势对自然感染白斑综合征病毒的抗病力分析[J] .水产学报,20.7.31(1):68-75.
[35] 李勇,李思发,王成辉,等 .三水系中华绒螯蟹形态判别程序的建立和使用[J] .水产学报,20.1.25(2):120-126.
[36] 梁前进,彭奕欣,余秋梅 .野生鲫和五个金鱼品种的判别分析和聚类分析[J] .水生生物学报,19.8.22(3):236-243.
[37] 林红,夏德全,杨弘,等 .遗传连锁图谱及其在鱼类遗传育种中的应用[J] .中国水产科学,20.0.7(1):95-98.
[38] 刘贵周,蔡传涛,罗媛,等 .不同混农林种植模式下糖胶树生物量与生长规律研究[J] .中国生态农业学报,20.8.16(1):150-154.
[39] 刘萍,孔杰,李健 .中国对虾精子作载体将生长激素基因导入受精卵的研究[J] .中国水产科学,19.6.3(1):6-10.
[40] 刘萍,孔杰,石拓,等 .暴发性流行病病原对中国对虾亲虾人工感染及对子代影响的PCR检测[J] .海洋与湖沼,19.9.30(2):139-144.
[41] 刘萍,孔杰,王清印,等 .显微注射生长激素基因导入中国对虾受精卵的研究[J] .中国水产科学,19.6.3(4):35-38.
[42] 刘萍,孟宪红,孔杰,等 .中国对虾微卫星DNA多态性分析[J] .自然科学进展,20.4.14(2):150-155.
[43] 刘小林,常亚青,相建海,等 .虾夷马粪海胆早期生长发育的遗传力估计[J] .中国水产科学,20.3.10(3):208.2.1 .
[44] 刘小林,常亚青,相建海,等 .栉孔扇贝不同种群杂交效果的初步研究Ⅰ .中国种群与俄罗斯种群的杂交[J] .海洋学报,20.3.25(1):93-99.
[45] 刘小林,常亚青,相建海,等 .栉孔扇贝壳尺寸性状对活体重的影响效果分析[J] .海洋与湖沼,20.2.33(6):673-678.
[46] 刘小林,吴长功,张志怀,等 .凡纳对虾形态性状对体重的影响效果分析[J] .生态学报,20.4.24(4):857-862.
[47] 刘志刚,王辉,符世伟 .湛江北部湾养殖墨西哥湾扇贝的形态增长规律[J] .水产学报,20.7.31(5):675-681.
[48] 楼允东 .鱼类育种学[M] .北京:中国农业出版社,1999.
[49] 卢立昌一 .エウうイエビの種苗生产[J] .调査研究ニエース,1984,17-21.
[50] 鲁绍雄,吴常信,连林生.性状遗传力与QTL方差对标记辅助选择效果的影响[J] .遗传学报,20.3.30(11):989-995.
[51] 陆彤霞,尤仲杰,陈清建 .浙江海域墨西哥湾扇贝生长的研究[J] .宁波大学学报(理工版),20.3.16(2):131-135.
[52] 栾生,孙悬玲,孔杰 .刺参耳状幼体体长遗传力的估计[J] .中国水产科学,2006,13(3):378-383.
[53] 罗坤,杨国梁,孔杰,等 .罗氏沼虾不同群体杂交效果分析[J] .海洋水产研究,20.8.29(3):67-73.
[54] 聂宗庆,王素平,李木彬,等 .盘鲍引进养殖与人工育苗试验[J] .福建水产,1995,1:9-16.
[55] 钱荣华,李家乐,董志国,等 .中国五大湖三角帆蚌形态差异分析[J] .海洋与湖沼,20.3.34(4):436-443.
[56] 钱志林 .坚定不移地搞好对虾养殖越冬工作[J] .中国水产,1990,10:4-5.
[57] 邱高峰 .虾蟹类遗传育种学研究[J] .水产学报,19.8.22(3):265-274.
[58] 盛志廉,陈瑶生 .数量遗传学[M] .北京:科学出版社,2001.
[59] 孙昭宁,刘萍,李健,等 .RAPD和SSR两种标记构建的中国对虾遗传连锁图谱[J] .动物学研究,20.6.27(3):317-324.
[60] 谭海东,张波,郝景泉,等 .转基因鱼的研究进展[J] .大连水产学院学报,1999,14(2):54-61.
[61] 田传远,王如才,梁英 .6-DMAP诱导太平洋牡蛎三倍体—抑制受精卵第二极体释放[J] .中国水产科学,19.9.6(2):1-4.
[62] 田燚,孔杰,栾生,等 .中国对虾生长性状遗传参数的估计[J] .海洋水产研究,20.8.29(3):1-6.
[63] 田燚,孔杰,杨翠华,等 .中国对虾形态性状与体重的相关性分析[J] .海洋与湖沼,20.6.37(增刊):54-59.
[64] 童金苟,朱嘉濠,吴清江 .鱼类和水生动物基因组作图研究的现状及前景[J] .水产学报,20.1.25(3):270-278.
[65] 汪德耀,刘汉英 .牡蛎人工杂交初步研究[J] .动物学报,19.9.11(3):283-295.
[66] 王和勇,陈敏,廖志华,等 .RFLP、RAPD、AFLP分子标记及其在植物生物技术中的应用[J] .生物学杂志,19.9.16(4):24-25.
[67] 王辉,刘志刚,符世伟 .湛江北部湾海域养殖墨西哥湾扇贝重量性状增长规律的研究[J] .热带海洋学报,20.7.26(5):53-59.
[68] 王清印 .海洋生物技术在海水养殖动植物品种培育和病害防治中的应用[J] .生物工程进展,19.6.16(6):41-48.
[69] 王清印 .养殖对虾的优良品种选育与海洋生物技术[R] .海洋高新技术产业化高级论坛,2000:192-201.
[70] 王绍中,茹天祥 .丘陵红粘土旱地冬小麦根系生长规律的研究[J] .植物生态学报,19.7.21(2):175-190.
[71] 王素娟,等 .海藻生物技术[M] .上海:上海科学技术出版社,1994.
[72] 王堉,等 .对虾人工育苗试验[J] .海洋水产研究丛刊,1965,20:34-50.
[73] 王堉,等 .对虾人工越冬及提前产卵的试验[J] .海洋水产研究丛刊,1965,20:22-23.
[74] 魏开建,熊邦喜,赵小红,等 .五种蚌的形态变异与判别分析[J] .水产学报,2003,27(1):13-18.
[75] 吴彰宽等 .胜利原油对对虾受精卵及幼体发育的影响[J] .海洋科学,1985,2:35-39.
[76] 吴仲庆,徐福章,周雪芳 .长毛对虾体长和体重的一些遗传参数[J] .厦门水产学院学报,19.0.12(2):5-14.
[77] 相建海,周令华,刘瑞玉,等 .中国对虾四倍体诱导研究[J] .海洋科学,1992,(4):55-61 .
[78] 相建海 .海水养殖生物病害发生与控制[M] .北京:海洋出版社,2001.
[79] 徐鹏,周岭华,相建海 .用PCR法快速筛选中国对虾含微卫星的重组阳性克隆[J] .水产学报,20.1.25(1):127-130.
[80] 杨青华,高尔明,马新明 .砂姜黑土玉米根系生长发育动态研究[J] .作物学报,20.0.26(5):587-593.
[81] 袁志发,周敬芋,郭满才,等 .决定系数—通径系数的决策指标[J] .西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版),20.1.29(5):131-133.
[82] 袁志发,周敬芋 .多元统计分析[M] .北京:科学出版社,2002:130-131.
[83] 张春艳,沈忠,周志权,等 .波尔山羊羔羊生长发育规律研究[J] .华中农业大学学报,20.6.25(6):640-644.
[84] 张德水,陈受宜 .DNA分子标记、基因组作图及其在植物遗传育种上的应用[J] .生物技术通报1998,5:15-22.
[85] 张建森,孙小异,施永红,等 .建鲤品种特性的研究[A]//建鲤育种研究论文集,北京:科学出版社,1994,27-39.
[86] 张琪,丛鹏,彭励 .通径分析在Excel和SPSS中的实现[J] .农业网络信息,2007,3:109-111.
[87] 张天时,刘萍,李健,等 .用微卫星DNA技术对中国对虾人工选育群体遗传多样性的研究[J] .水产学报,20.5.29(1):6-12.
[88] 张天时,刘萍,李健,等 .中国对虾与生长性状相关微卫星DNA分子标记的筛选[J] .海洋水产研究,20.6.27(5):34-38.
[89] 张天时,王清印,刘萍,等 .中国对虾人工选育群体不同世代的微卫星分析[J] .海洋与湖沼,20.5.36(1):72-80.
[90] 张炎,邓其祥 .铜鱼生长规律的数学模型[J] .四川师范学院学报(自然科学版),19.6.17(1):31-34.
[91] 张尧庭,方开秦 .多元统计分析引论[M] .北京:科学出版社,1982.
[92] 张永普,林志华,应雪萍 .不同地理种群泥蚶的形态差异与判别分析[J] .水产学报,20.4.28(3):339-342.
[93] 张玉勇,常亚青,宋坚 .杂交育种技术在海水养殖贝类中的应用及研究进展[J] .水产科学,20.5.24(4):39-41.
[94] 赵晓临,王旭 .北方池养中国对虾生长特性研究[J] .水产学杂志,20.7.20(2):50-53.
[95] 周百成,曾呈奎 .藻类生物技术与海洋产业发展[J] .生物工程进展,19.6.16(6):13-16.
[96] 周茂德,高允田,吴融,等 .太平洋牡蛎与近江牡蛎、褶牡蛎人工杂交的初步研究[J] .水产学报,19.2.6(3):235-241.
[97] Ahmed M,Abbas G. Growth parameters of the f inf ish andshellf ish juveniles in the tidal waters of Bhanbhore,Korangi Creek and Miani Hor Lagoon[J]. Pakistan Journal of Zoology,20.0.32(3-4):32-331.
[98] Alcivar-Warnen A. Efforts towards developing a linkagemap for penaeidshrimp [A]. Grant D, Lazo G R. . eds:Plant and Animal Genome[C]. San Diego: Scherago Co,1999. 35.
[99] Aras-hisar S,Yanik T,Hisar O,et al. Hatchery and growth performance of two trout pure breeds,Salvelinus alpinus and Salmo trutta fario,and their hybrid[J]. Israeli J Aquac Bamidgeh,20.3.55(3):154-160.
[100] Argue B J,Aree S M,Lotz J M,et al. Selective breeding of Pacif ic whiteshrimp(Litopenaeus vannamei)for growth and resistance to Taura Syndrome Virus[J]. Aquaculture,2002,204:447-461.
[101] Argue B J,Liu Z,Dunham R A. Dress-out and f illet yields of channel catf ish,Ictalurus punctatus,blue catf ish,Ictalurus furcatus,and their F1,F2 and backcross hybrids[J]. Aquaculture,2003,228:81-91.
[102] Aulstad D,Gjedrem T,Skjervold H,et al. Genetic and Environmental Sources of Variation in Length and Weight of Rainbow Trout (Salmo gairdneri)[J]. Journal of the Fisheries Research Board of Canada,19.2.29(3):237-242.
[103] Bashirullah A K M,Mahmood N,Matin A K M A. Aquaculture and coastal zonemanagement in Bangladesh[J]. CoastalManage,1989,17:119-128.
[104] Benzie J A H,Kenway M,Ballment S,et al. Interspecif ic hybridization of the tiger prawns Penaeusmonodon and Penaeus esculentus[J]. Aquaculture,1995,133:103-112.
[105] Benzie J A H,Kenway M,Trott L. Estimates for the heritability ofsize in juvenile Penaeusmonodon prawns from half-sibmating[J]. Aquaculture,1996,152:49-54.
[106] Benzie J A H,Kenway M.Trott L.Estimates for the heritability ofsize in juvenile Penaeusmonodon prawns from halfsibmating[J]. Aquaculture,1996,152:49-54.
[107] Benzie J A H. Penaeid genetics and biotechnology[J]. Aquaculture,1998,164:23-48
[108] Bienfang P K,Sweeney J N. The use of SPF broodstock to prevent disease inshrimp farming[J]. Aquaculture Asia,20.1.6(1):12-15.
[109] Bray W A,Lawrence A L,Lester L J, et al. Increased larval production of penaeussetiferus by artif icial insemination dutingsourcing cruises[J]. Journal of the World Mariculture Society,19.2.13(1-4):121-133.
[110] Brock J A,Gose R B,Lightner D V,Hasson K. Recent developments and an overview of Taura Sndrome of farmedshrimp in the Americas[C]. In:Flegel,T. W. ,MacRae,I. H. Eds. ,Diseases in Asian Aquaculture Ⅲ . Fish Health Section,Asian Fisheries Society,Manila,Philippines,1997,275-284.
[111] Bryden C A,Heath J W,Heath D D. Performance and heterosis in farmed and wild Chinooksalmo (Oncorhynchus tshawyacha)hybrid and purebred crosses[J]. Aquaculture,2004,235:249-262.
[112] Carlberg J M,Vanolst J,Ford R. A comparison of larval and juvenilestages of the lobsters Homarns americanus Homarus gammarus and their hybrids[J]. Proceedings of the annualmeeting-World Mariculture Society,19.8.9(1-4):109-122.
[113] Carr W H,Fjalestad K T,Godin D,et al. Genetic variation in weight andsurvival in a population ofspecif ic pathogen-freeshrimp,Penaeus varmamei[C]//Flegel T W,Macrae I H. Diseases in Asian Aquaculture Ⅲ . Manila,Philippines:Fish Health Sectiwi,Asian Fisheries Society,1997:265-271.
[114] Chevassus B. Variability heritability des performances de:croisvsance chez truite arcen-ciel (S. gairdneri)[J]. Ann Genet Sel Anim,1976,8:273-282.
[115] Chew S. Artif icial insemination using preservedspermatophores in palaemonialshrimp Macrobrachium rosenbergii[J]. Bulletin of the Japanese Society of Entif ic Fisheries,19.2.48(12):1693-1695.
[116] Crenshaw J W,Heffeman P B,Walker R L. Heritability of growth rate in thesouthern Bayscallop,Argopecte nirradiam concentricus[J]. Journal of Shellf ish Research,1991,10:55-64.
[117] De Tomas Kutz A,Lawrence A L. Quantitative genetic analysis of growth andsurvival in Penaeus vannamei versus temperature[C]. Proceedings1st Latin American Shrimp Farming Congress,Panama:1998.
[118] David L,Leighton, Cindy A,Lewis. Experimental hybridization in abalones[J]. International Journal of Invertebrate Reproduction,20.2.5(5):273-282.
[119] Doupe R G,Lymbery A J,Greeff J. Genetic,et al. varation in the growth traits ofstraight-bred and crossbred black bream (Acanthopagus butcheri Munro)at 90 days of age[J]. Aquaculture Research,20.3.34(14):1297-1302.
[120] Emmanuel Goyard Jacques Patrois Jean-Marie Peignon et al. IFREMER’s Shrimp Genetic's Program[J]. The Advocate,19.9.2(6):26-29.
[121] Gall G A E. Genetics of reproduction in domesticated rainbow trout[J]. Journal of Animalence,19.5.40(1):19-28.
[122] Gao T X,LI J,Wang Q Y,et al. Partialsequence analysis ofmitochondrial COI gene of the Chinese shrimp,Fenneropenaeus chinensis [J]. Journal of Ocean University of Qingdao,20.3.2(2):167-171.
[123] Gitterle T,Rye M,Salte R,et al. Genetic(co)variation in harvest body weight andsurvival in Penaeus(Litopenaeus)vannamei understandard commercial conditions[J]. Aquaculture,2005.2.3(1-4):83-92.
[124] Gjedrem T,Fimland E. Potential benef its from high health and genetically improvedshrimpstocks[C]. In:Browdy C L,Hopkins J S Eds. Swimming through troubled water,proceedings of thespecialsession onshrimp farming. World Aquaculture Society,BatonRouge,L A,1995,60-65.
[125] Gjerde B R,Reddy P V,Mahapatra K D,et al. Growth andsurvival in two complete diallele crosses with f ivestocks of rohu carp (Labeo rohita)[J]. Aquaculture,2002,209(1/4):103-116.
[126] Gjerde B. Genetic variation in production traits of Atlanticsalmon and rainbow trout[C]. 32nd Annual Meeting of the European Association for Animal Production,in Zagreb,Yugoslavia,1981,Ⅳ -16.
[127] Goyard E,Patrois J,Peignon J M,et al. Selection for better growth of Penaeusstylirostris in Tahiti and New Caledonia[J]. Aquaculture.2002,204:461-469.
[128] Gunnes K,Gjedrem T. A genetic analysis of body weight and length in rainbow trout reared inseawater for18months[J]. Aquaculture,1981,24:161-175.
[129] Gunnes K,Gjedrem T. Selection experiments withsalmonⅣ Growth of Atlanticsalmon during two years in thesea[J]. Aquaculture,1978,5:19-24.
[130] Harue K,Mutsuyshi T,Katsuya M,et al. Estimation of body fat content fromstandard body length and body weight on cultured redsea bream [J]. Fisheries Science,2000,66(2):365-372.
[131] Hena M A,Kamal M,Mair G G. Salinity tolerance insuperior genotypes of tilapia,Oreochromis niloticus,Oreochromismossambicus and their hybris[J]. Aquaculture,2005,247:189-211.
[132] Hetzel D J S,Crocos P J,Davis G P,et al. Response toselection and heritability for growth in the Kuruma prawn,Penaeus japonicus [J]. Aquaculture,2000,181:215-224.
[133] Ibarra A M,Ramirez J L,Ruiz C A et al. Realized heritabilities and genetic correlation after dualselection for total weight andshell width in catarinascallop (Argopecten ventricosus)[J]. Aquaculture,1999,175:227-242.
[134] Jim Wyban. Breedingshrimp for fast growth and virus resistance[J]. The Advocate,20.0.3(6):32-34.
[135] Kenneth Jones. Improvingshrimpstocks withmicrosatellites[J]. The Advocate,2000,3(6):35-37.
[136] Langdon C J,Jacobson D P,Evans F,et al. Themolluscan broodstock program improving Pacif ic oyster broodstock through geneticselection[J]. Journal of Shellf ish Research,20.0.19(1):616.
[137] Lee C H,Mark R Y,Philip J B. Growth characteristics of freshwater pearlmussels Margaritiferamargaritifera (L. )[J]. Freshwater Biology,2000(43):243-257.
[138] Lester L J. Developing aselective breeding plan for penaeidshrimp[J]. Aquaculture1983,33:41-51.
[139] Li ZhX,Li J,Wang Q Y,et al. AFLP-based genetic linkagemap ofmarineshrimp Fenneropenaeus chinensis[J]. Aquaculture,2006,261:463-473.
[140] Li Zh X,Li J,Wang Q Y,et al. The effects ofselective breeding on the geneticstructureshrimp Fenneropenaeus chinensis populations[J]. Aquaculture,2006,258:278-283.
[141] Lightner D V,Hasson K W,White B L,et al. Experimental infection of western hemisphere penaeidshrimp with asian whitespotsyndrome vi rus and asian yellow head vims[J]. Journal of Aquatic Animal Health,1998,10:271-282.
[142] Lin M NI,Ting Y. Spermatophore transplantation and artif icial fertilization in grassshrimp[J]. Nippon Suisan Gakkaishi,1986,52:585-590.
[143] Liu B Z,Liang Y B,Liu X L,et al. Quantitative traits correlative analysis and growth comparison among different populations of bayscallop,Argopecten irradians[J]. Acta Oceanological Sinica,20.4.23(3):533-541.
[144] Liu P,Kong J,Shi T,et al. RAPD analysis of wildstock of penaeidshrimp (Penaeus chinensis)in Chinese coastal waters of the Huanghai Sea and coastal waters of the Bohai Sea[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica,2000:119-126.
[145] Mallet A L,Freeman K R,Dickie L M. The genetics of production characters in the bluemussel Mytilus eclulis I. A preliminary analysis[J]. Aquaculture,1986,57:133-141.
[146] Misamore M,Browdy C L. Evaluating hybridization potential between Penaeussetiferus and Penaeus vannamei through naturalmating,artif icial insemination and in vitro fertilization[J]. Aquaculture,1997,150:1-11.
[147] Moore S S,W,han V,Davis G,et al. The development and application of geneticmarkers for the Kururma prawn Penaeus japonicus[J]. Aquaculture,1999,173:19-33.
[148] Nguenga D,Teugels G G,Ollevier F,et al. Fertilization,hatching,survival and growth rates in reciprocal crosses of twostrains of an African catf ish Heterobranchus longif ilis Valenciennes1840 under controlled hatchery conditions[J]. Aquaculture Research,20.0.31(7):565-573.
[149] Paul K,Bienf ang,Sweeney N J. The use of SPF broodstock to prevent disease inshrimp farming[J]. Aquaculture Asia,20.1.6(1):12-15.
[150] Peharda M,Christopher A R,Vladimir O,et al. Age and growth of the bivalve Arca noae L. in the Croatian Adriatic Sea[J]. Journal of Molluscan Studies,2002(68):307-311.
[151] Pejrez-Rostro C I,Ramirez J L,Ibarra A M. Maternal and cage effects on genetic parameter estimation for Pacif ic whiteshrimp Penaeus Vannamei Boone[J]. Aquaculture Research,1999,30:1-14.
[152] Persyn H O. Artif icial insemination ofshrimp L . S [P]. Patent4031855,June,28,1978.
[153] Quinton C L,Mckay L R,Mcmillan I. Strain andmaturation effects on femalespawning time in diallel cross of threestrains of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchusmykiss)[J]. Aquaclture,2004.2.4(1/4):99-101.
[154] Rawson P D,Hilbish T J . Heriiability of juvenile growth for hard clam Mercenariamerce naria[J]. Marine Biology,1990.1.5(3):429-437.
[155] Refstie T,Steine T A. Selection experiments withsalmon Ⅲ Genetic and environmentalsources of variation in length and weight of Atlanticsalmon in the freshwater phase[J]. Aquaculture,1978,14:221-232.
[156] Refstie T. Genetic and environmentalsources of variation in body weight and length of rainbow trout f ingerlings[J]. Aquaculture,1980,19:351-358.
[157] Sandifer P A,Lawrence A L,Harris S G,et al. Electricalstimulation ofspermatophore expulsion inmarineshrimp,Penaeusspp[J]. Aquaculture,19.4.41(2):181-187.
[158] Sandifer P A,Lynn J. Artif icial insemination of carideanshrimp. In: Clark W H,Adams H S,eds. Recent advances in invertebrate reproduction[C]. Elsevier,Amsterdam,The Netherlands.1980,271-289.
[159] Sbordonia V,Matthaeis E D,Sbordonib M C,et al. Bottleneck effects and the depression of genetic variability in hatcherystocks of Penaeus japonicus (Crustacea,Decapoda)[J]. Aquaculture,19.6.57(1-4):239-251.
[160] Shokita S. Larval development of interspecif ic hybrid between Machrobrachium asperulum from Taiwan and Marobrachiumshokitai from the Ryukyus[J]. Bulletin of t he Japanese Society of Scientif ic Fisheries,1978,44:1187-1196.
[161] Su G S,Liljedahl L E,Gall G A E. Genetic and environmental variation of female reproductive traits in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchusmykiss)[J]. Aquaculture,1997,154(97):115-124.
[162] Tariq A,Khan et al. INFOFISH International[J]. Biology,2000,1:41-45.
[163] Tassanakajan A,Tiptamonnukal A,Supungul C. Isolation and characterization ofmicrosatellitemarkers in the black tiger prawn (P.monodon)[J]. Mol Mar Biol Biotechn,1999,7:55-62.
[164] Tave D,Smitherman R O. Predicted response toselection for early growth in Tilapia JiiLotica[J]. Transactions of the American Fisheries Society,1980,109:439-456.
[165] ToroJ E,Aguila P,Vergara A M. Spatial variation in response toselection for live weight andshell length from data on individually tagged Chilean native oysters (Ostrea chilemis Philippi,1845)[J]. Aquaculture,1996,146:27-37.
[166] ToroJ E,Newkirk G E. Divergentselection for growth rate in the European oyster (Ostrea eciulis):Response toselection and estimation of genetic parameters[J]. Marine Ecology Progress Series,1990,62:219-226.
[167] Urmaza E B,Aguilar R O. Growth performance ofsaline-tolerant tilapia produced from cross combinations of various tilapiaspieces[J]. Journal of Aquaculture Tropics,20.5.20(1):11-28.
[168] Vandeputte M,Quillet E,Chevassus B. Early development andsurvival in brown trout (Salmo trutta fario L. ):Indirect effects ofselection for growth rate and estimation of genetic parameters[J]. Aquaculture,2002,204:435-446.
[169] Wada K T. Geneticselection forshell traits in Japanese pear oyster,Pimtada fucatamartemi [J]. Aquaculture,1986,57:171-177.
[170] Wang W J,Kong J,Bao Z M,et al. Isozyme variation in four populations of Fenneropenaeus chinensisshrimp[J]. Biodiversity Science,20.1.9(3):241-247.
[171] Wolfus G M,Garcia D K Alcivar-Warren A. Application of themicrosatellite technique for analysin gentic diversity inshrimp breeding program[J]. Aquaculture,1997,152:35-48.
[172] Wyban J. Breedingshrimp for fast growth and virus resistance[J]. The Advocate,2000,3(6):32-34.
[173] Xiang J H Clark W H Griff in F,et al. Study on feasibility of chromosomesetmanipulations in themarineshrimpsicyonia in gentis[R]. International Crustacea Conference. Brisbane,Australia,1991.
[174] Zhaoxia Li,Jian Li,Qingyin Wang,et al. AFLP-based genetic linkagemap ofmarineshrimp Fenneropenaeus chinensis[J]. Aquaculture,2006,261:463-473.
[175] Zhaoxia Li,Jian Li,Qingyin Wang,et al. The effects ofselective breeding on the geneticstructure ofshrimp Fenneropenaeus chinensis populations[J]. Aquaculture,2006,258:278-283.
免责声明:以上内容源自网络,版权归原作者所有,如有侵犯您的原创版权请告知,我们将尽快删除相关内容。















