比较概念性测评框架和测评三角,两者都是建立在“测评本质是基于证据推断过程”的理解之上。对建立高效的测评系统,两者分别考虑了相关的要素。两者基本要素的对应,如表3-1所示。
表3-1 概念性测评框架和测评三角基本要素对应表
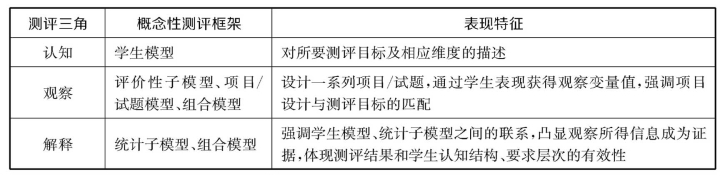
从上述对应关系可知,测评三角是概念性测评框架的简化和组合(两者内在存在着很强的对应性和一致性),是基于证据为中心的测评设计模式发展的产物。
本书利用测评三角的三个要素 —— 认知、观察、解释,构建测评系统比较分析的框架,并作为测评在系统层面比较分析的维度,对大规模国际数学测评系统进行比较分析。具体而言,“认知”指的是测评的目标及相关目标维度设计;“观察”指的是测评试题设计,即一系列项目/试题,通过学生表现获得观察变量值,强调项目设计与测评目标的匹配,本书中尤其注重题型使用、编码系统设计及测评蓝图的呈现;“解释”强调的是学生模型、统计子模型之间的联系,将观察所得的信息变为证据,体现测评结果和学生认知结构、要求层次的有效性。因此,本书主要着力于形成量尺和相应的基准或精熟度层次,并在这个过程中运用、解释IRT统计模型。
下面,在对PISA、 TIMSS及以中考数学为例的国内大规模数学测评进行分析时,会将上述测评三角所示的三个要素作为比较的维度,并充分予以利用。通过比较上述大规模测评在三个维度上的差异性,以及梳理上述大规模测评在三个维度之间内在的关系,尝试解答本书第一章提出的问题,并力求达到本书的研究目标。
【注释】
[1]Cohen, R.J., Montague, P., Nathanson, L. & Swerdlik, M.E.P.sychlolgical testing: An introduction to tests and measurement[M].Mlayfield,CA: Mountain View, 1998:76.
[2]Ebel,R.L..Measurement and the teacher, in Aiken.L.R.Jr.(eds).Readings in psychological and educational testing[M].Boston :Allyn and Bacon, 1973.10.
[3]Lord,F.M. & Novick,M.R.S.tatistical theories of mental test scores[M].Reading, MA:Addison Wesley Publishing Company,1968.
[4]参见:
Goleman,D..Emontional interlligence[M].New York:Bantam Books,1995.
Sternberg, R.J.T.he triarchic mind LA new theory of human intelligence[M].Mew York: Viking Press, 1998.
Sternberg,R.J.I.n search of the human mind[M].Ft.Worth, TX: Harcourt Brace, 1995.
[5]Sternberg,R.J.S.pecial issue on intelligence and lifetime learning[J].American Psychologist, 1997, 52 (10) : 1032.
[6]Cronbach, L.J., Ambron, S.R., Dombusch, S.M., Hess, R.D., Hornik, R.C., Walker, D.E. & Weiner, S.S..Toward a reform of program evaluation[M].San Francisco: Jossey-Bass, 1980:112.
[7]Scriven, M.S..Evaluation thesaurus[M].Newbury Pack, CA: Sage.
[8]杨向东.教育测量在教育评价中的角色[J].全球教育展望,2007(11):22.
[9]Stufflebeam,D.L. & Shinkfield, A.J..Systematic evaluation[M].Norwell, MA: Kluwer -Nijhoff,1985: 56.
[10]杨向东教育测量在教育评价中的角色[J].全球教育展望,2007(11):21.
[11]Gulliksen, H..Measurement of learnig and mental abilities[J].Psychometrika,1961(26):95.
[12]Messick, S.The interplay of evidence and consequences in the validation of performance assessments [ J ].Educationcal Researcher, 1992,23(2):17.
[13]Mislevy,R.J.(1994).Evidence and inference in educational assessment[J].Psychometrika, 1994( 12): 341—369.
[14]Schum,D.A..Evidence and inference for the intelligence analyst[M].Lanham, MD: University Press of America,1987:16.
[15]参见:
Missick, S..The interplay of evidence and consequences in the validation of performace assessments[ J].Educational Researcher, 1992,23(2):13—23.
Mislevy, R.J.E.vidence and inference in educational assessment[J].psychometrika,1994(59):439—483.
Mislevy, R.J.P.robability-based inference in cognitive diagnosis.in P.Nichols, S.Chipman, & R.Brennan(eds).Cognitively diagnositic assessment[C].Hillsdale, NJ: Erlbaum, 1995:43—71.
[16]Robert J.Mislevy, Linda S.Steinberg, & Russell G.Almond.E.vidence-centered assessment design.http://www.education.umd.edu/EDMS/mislevy/papers/ECD_overview.html .2015-02-04.
[17]Robert J.Mislevy, Michelle M.Riconscence.E.vidence-centered assessment design: layers, structures, and terminology.PADI Technology Report 9.CA:SRI International,2005.
[18]Robert J.Mislevy, Michelle M.Riconscence.E.vidence-centered assessment design.Handbook of Test Development[M].Lawrence erlvaum associates, 2006:37.
[19]Mislevy,R.J., Steinberg, L.S., & Almond, R.G.(in press).On the several roles of task model varables in assessment design[EB/OL].http://files.eric.ed.gov/fulltext/ED431804.pdf.2014-06-28.
[20][美]德内拉·梅多斯著,邱昭良译.系统之美—— 决策者的系统思考[M].浙江:浙江人民出版社,2012:18.
[21]National Research Council. National Science Education Standards[ M].Washington.DC: National Academy Press,1996:67.
[22]National Research Council.Knowing What Students Know: The Science and Design of Educational Assessment[M] .Washington.DC:National Academy Press, 2001:53.
[23]National Research Council.Knowing What Students Know: The Science and Design of Educational Assessment[M].Washington.DC: National Academy Press, 2001: xi.
[24]National Research Council.Knowing What Students Know: The Science and Design of Educational Assessment[M].Washington.DC: National Academy Press, 2001:42.
免责声明:以上内容源自网络,版权归原作者所有,如有侵犯您的原创版权请告知,我们将尽快删除相关内容。















