第三节 浙江产业集群企业营销绩效分析
本节将根据营销绩效的评价模型,通过模糊评价的方法对从属不同产业集群下的A、B企业的营销绩效进行评价。
模糊综合评价是将模糊评判和层次分析结合起来,是对多目标层次下多属性、多相关因素进行综合考虑的评价方法。模糊综合评价法最大的特点是将定性指标数量化及各指标的无量纲化,使定性和定量指标有机地结合起来,从而反映企业营销绩效各评价指标的总体表现。
本书在运用层次分析法确定评价体系各指标的权重后,进一步采用该方法对营销绩效进行模糊评价。
营销绩效模糊评价模型如下:
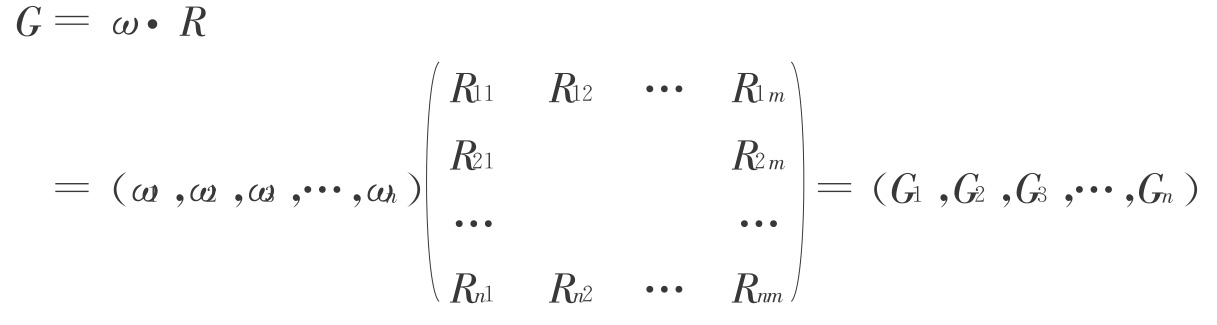
其中:ω为指标权重系数阵;
R为指标评分矩阵;
G为指标评价阵。
企业在营销绩效评价时,请测评人员就评价指标集确定各因素的隶属度,从而建立指标评分矩阵R。在本模型中评价指标集由指标体系的各指标项构成,记为:U={u1,u2,…,un},其中u1,u2,…,un分别代表产品质量、价格竞争力直至集群品牌的各指标项;用以确定因素隶属度的因素评判语集由好、较好、一般、较差和差的5分法构成;单因素ui=(i=1,2,…,n)隶属度反映的是专家组对该因素在评判语集判断中的分布情况,评分矩阵R即由各因素的隶属度集合而成。另外,模型中的指标权重系数阵ω即为我们已确定的指标体系权重总排序中的权重系数。
模型应用选择了从属不同产业集群的两家企业(海利得新材料股份有限公司、兰亭针织有限公司,本书分别以A、B企业代替)进行营销绩效比对,向企业内部中高层管理人员(销售总监/经理以上)及外部专家发放调查问卷,调查问卷发放规模为5份。在定量指标如产品质量、价格竞争力、服务与技术支持等的处理上,由测评人员根据企业、行业及市场实际做出主观判断;对于定量指标则建议参考2008年企业历史数据。由于涉及商业秘密,本研究中的引用数据经过了一定调整。
1.A、B企业简介
A企业是一家以聚酯工业纤维、灯箱广告材料为主的集生产、销售、科研于一体的高新技术企业,产品销售涉及美洲、欧洲、东南亚及中东等50余个国家和地区,2008年已在中小企业板成功上市。A企业所属产业集群是浙江省开发较早的产业集群,所辖园区已成为浙江区域名牌,其基础设施、服务配套体系完善,目前正在构建以自主创新、产业结构优化升级为核心的特色产业集群,力争打造世界级品牌。
B企业是一家生产全涤、全棉针织及印花布面料为主的新兴企业,具有自主出口经营权,在所在集群中比较有代表性。B企业所属产业集群已列入国家大力发展的特色产业集群名录,以轻纺市场、印染配套为产业优势,形成了针织、纺织、绣花为主的三大工业区块,被中国纺织工业协会授予“中国针织名镇”称号。
2.A、B企业营销绩效评价
首先对A企业进行营销绩效的评价,经问卷调查后得到的评价矩阵如表7‐28所示。
表7‐28 A企业营销绩效评价矩阵

续表

由表7‐28得到24个因素的评价矩阵R如下:

已知各因素总排序权重ω:
ω=(0.01598 0.00578 0.00663…0.00612 0.01885 0.06838)
于是GA=ω·R=(0.49 0.42 0.08 0 0)
在此我们可以根据最大隶属度原则确定该企业营销绩效的综合评价等级,如A企业的营销绩效水平属领先,处于好与较好之间;我们也可以进行单值化处理,即根据评判语集将各等级赋值如V=(5,4,3,2,1)T
则企业A的单值综合评价结果为PA=GA·V=5.29
按照同样的思路,我们可以对B企业进行营销绩效的评价,B企业评价矩阵见附录。于是可得:
GB=(0.06 0.27 0.61 0.06 0)
PB=3.23
这样,不仅A、B企业可以独立研判影响营销绩效的薄弱环节及其影响程度,也可进行企业间的比对分析,认识企业的相对市场表现并采取进一步的措施。如我们可从单值综合评价结果分析中的一个方面举例:评价结果显示PA>PB,这说明A企业的营销绩效要明显优于B企业,此评价结果与企业的实际水平是相符的。事实上,A企业是具有中国名牌、浙江名牌、产品质量免检、国家级火炬计划项目的产业龙头企业,其灯箱广告材料的产能居全国第二,涤纶工业长丝产能更是居全球前十名,企业被《福布斯》杂志评为2007中国最具发展潜力的产业100强。而A企业所属的产业集群也拥有多项荣誉称号,曾荣登中国最具商业影响力专业市场榜榜单;集群的高新技术项目、信息化建设项目、专业技术市场项目都有扎实的基础,其咨询、培训、研发、对外交流等方面也走在全国纺织行业的前列。反观B企业,虽具有发展潜力但规模较小、技术实力不强,在产品研发、市场运作、内部管理及企业家认识等方面尚有诸多不足;企业所属集群虽已列入产业重点发展名录并建立了相关产业园区,但毕竟基础相对薄弱,产业的软硬件辅助设施尚不完备,产业还处于分块经营的状态,且业内企业普遍规模较小,产业集群的整体优势目前还难以发挥,对企业发展的推动作用有限。
参考文献
[1]孙淑英.入世后我国企业营销绩效评价的变革研究[J].北京理工大学学报,2005(10).
[2]王秀村.企业营销绩效评价的国际比较[J].中国管理科学,2004(1).
[3]王利政.企业持续营销能力结构的研究[J].工业技术经济,2007(5).
[4]田明泓.企业营销绩效的财务评价分析[J].市场论坛,2004(4).
[5]吴晓云.全球营销战略模型的检验指标创建及其应用[J].管理科学学报,2006(2).
[6]傅小华.面向网络环境的企业营销绩效评价指标体系研究[J].武汉理工大学学报,2004(2).
[7]冯振环.隐性营销绩效评价指标体系与方法研究[J].生产力研究,2004(3).
[8]柳荣.市场难度在区域营销绩效分析中的评价和应用[J].中国管理信息化,2006(12).
[9]吴勇.营销渠道绩效研究述评[J].经济与管理,2007(9).
[10]司林胜.商业企业市场营销效益综合评价指标体系研究[J].山西财经学院学报,1997(5).
[11]王月辉.中国加入WTO后的市场环境变化与企业营销绩效的综合评价[J].哈尔滨工业大学学报,2002(12).
[12]王月辉.中国企业营销绩效评价操作中的有关题[J].北京理工大学报,2003(6).
[13]谢仲秋.营销效益评价指标体系的设计[J].统计与决策,2003(2).
[14]孙淑英.我国企业营销绩效评价指标体系构建的实证研究[J].中国软科学,2006(1).
[15]蔡宁.论产业集群竞争优势基础的转变[J].浙江大学学报,2003(11).
[16]陶金国.论产业集群的营销优势[J].财经问题研究,2003(11).
[17]菲利普·科特勒,凯文·莱恩·凯勒.营销管理(第12版)[M].上海:世纪出版集团,上海人民出版社,2006.
[18]宇传华.SPSS与统计分析[M].北京:电子工业出版社,2007.
[19]马庆国.管理统计[M].北京:科学出版社,2002.
[20]王重鸣.心理学研究方法[M].北京:人民教育出版社,2001.
[21]刘大海.SPSS15.0统计分析[M].北京:清华大学出版社,2008.
[22]柯惠新.调查研究中的统计方法[M].北京:中国传媒大学出版社,2005.
[23]杜栋.现代综合评价方法与案例精选[M].北京:清华大学出版社,2005.
[24]Ahn H.Applying the Balanced Scorecard Concept:An Experience Report[J].Long Rang Planning,2001(34):441‐461.
[25]Ambler T.Marketing and the Bottom Line[M].Pearson Education,London,2000.
[26]Ambler T.,D.Riley.Marketing Metrics:A Review of Per‐formance Measures in Use in the UK and Spain[J].London Business School,Working Paper.London,2000.
[27]Ambler T.,Kokkinaki F.Measures of Marketing Success[J].Journal of Marketing Management,1997(13):665‐679.
[28]Barwise,Patirck.Brand equity:nark or bijou?[J].International Journal of Research in Marketing,1993(10):93‐103.
[29]Bhargava M.,C.Dubelaar,S.Ramaswami.Reconciling Diverse Measures of Performance:A Conceptual Framework and Test of a Meth‐odology[J].Journal of Business Research,1994(3):235‐246.
[30]Birkinshaw J.M.,Morrison A.J.Configurations of strategy and structure in subsidiaries of multinational corporations[J].Journal of International Business Studies,1995,26(4):729‐754.
[31]Bonoma,Thomas V.,Clark Bruce H.Marketing performance assessment[M].Harvard Business School Press,Boston,1988:49‐67.
[32]Buzzell R.D.,B.T.Gale.The PIMS Principles:Linking Strategy to Performance[M],New York,The Free Press,1987.
[33]Bruce H.,Clark.Organizational motivation,opportunity and ability to measure marketing performance[J].Journal of Strategic Marketing,2005(13):241‐259.
[34]Bromnile,Douglas.Marketing Audits and Auditing:Diagnosis Through Intervention[J].Jounral of Marketing Management,1996(12):99‐11.
[35]Clark B.H.Marketing Performance Measures:History and Interrelationships[J].Journal of Marketing Management,1999(15):711‐732.
[36]Davidson J.H.Transforming the Value of Company Reports through Marketing Measurement[J].Journal of Marketing Manage‐ment,1999(15):757‐777.
[37]Dibbo,Benchmarking.Marketing from an Engineering Perspec‐tive[J].Journal of Marketing Management,1996(12):1‐6.
[38]Dowling G.R.,Uncles M.Do customer loyalty programs really work?[J].Sloan Management Review,1997(38):71‐82.
[39]Donald R.Lehmann,David J.Reibstein.Marketing Metrics and Financial Performance[J].Marketing Science Institute,2006(10):23‐25.
[40]Eccles,R.G.The Performance Measurement Manifesto[J].Harvard Business Review,1991(1):13‐137.
[41]Erik.Marketing Performance and Metrics[M].Helsinki School of Economics,2009.
[42]Feder,Robert A.How to measure marketing performance[J].Harvard Business Review,1965,43(5):132‐142.
[44]Gale,B.T.Managing Customer Value[M].Free Press,New York,1994.
[45]Geroge.S.Day,Robin Wesley.Assessing Advantage:A Frame‐work for Diagnosing Competitive Superiority[J].Journal of Marketing,1998(12):2‐20.
[46]Glazier,William,Robert Nelson,Don O'Sullivan.Measures and Metrics:The CMO Council Report[M].CMO Council,2004.
[47]Goodman,SamR.Techniques ofProf itabilityAnalysis,Wile‐Interscience[M].New York,1970:430‐467.
[48]David,Schmidt,Sandre L,Multisource effect on the satisfaction formation process[J].Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science,1999(2):114‐129.
[49]Ittner C.D.,Larcker D.F.Are Nonfinancial Measures Leading Indicators of Financial Performance?An Analysis of Customer Satisfac‐tion[J].Journal of Accounting Research,1998(36):1‐35.
[50]Ittner,C.D.,Larcker D.F.Innovations in Performance Meas‐urement:Trends and Research Implication[J].Journal of Management Accounting Research,1998(10):205‐238.
[51]Jaworski Bernard J.Toward a Theory of Markting Contorl:Environment Context,Control Types,and Consequences[J].Journal of Marketing,1988(52):23‐39.
[52]Jaworski,B.,Kohli,A.Market orientation:Antecedents and consequences[J].Journal of Marketing,1993,52(3):53‐70.
[53]James D.Lenskold.Marketing ROI:The Path to Campaign,Customer,and Corporate Prof itability[M].McGraw‐Hill,2003.
[54]John Davis.Measuring Marketing:103 Key Metrics Every Marketer Needs[M],Wiley,2006.
[55]Kaplan R.S.,Norton,D.P.Using the Balanced Scorecard as a Strategic Management System[J].Harvard Business Review,1996(2):75-85.
[56]Keh H.T.,Chu,S.,Xu J.Efficiency,effectiveness andproduc‐tivity of marketing services[J].European Journal of OperationalResearch,2006(170):265‐276.
[33]Keller,Kevin L.Strategic Brand Management[M].Pretice‐Hall,Upper Saddle River,NJ,USA,1998.
[57]Kohli,A.K.,Jaworski,B.J.Market Orientation:The Con‐struct,Research Propositions,and Managerial implications[J].Journal of Marketing,1990,54(2):1‐18.
[58]Kokkinaki F.,T.Ambler.Marketing Performance Assessment:An Exploratory Investigation intoCurrent Practice and the Role of Firm Orientation[J].Marketing Science Institute.Cambridge,MA.Working paper,1999:99‐114.
[59]Kotler Philip,Gregor William,Rodgers William.The marketing audit comes of age[J].Sloan Management Review,1977,18(2):25‐43.
[60]Levitt,T.After the Sale is Over[J].Harvard Business Review,1983(61):87‐93.
[61]Lysonski S.,A.Pecotich.Strategic Marketing Planning,Envi‐ronmental Uncertainty and PerformanceInternational[J].Journal of Research in Marketing,1992(9):247‐255.
[62]Marcin Pont and Robin Shaw.measuring marketing perform‐ance:a critique of empirical literature[J].A NZMAC 2003 Conference Proceedings A delaide 1-3,December 2003.
[63]Meyer M.W.Finding Performance:The New Discipline in Management[J].Performance Measurement‐Theory and Practice,1998(1),Cambridge,England:Centre for Business Performance,xiv‐xxi.
[64]Michael D.Hartline.Internal Relationship Management:Link‐ing Human Resources to Marketing Performance[J].Journal Relation‐ship Marketing,2004(3):1‐4.
[65]Malina M.A.,Selto F.H.Communicating and Controlling Strategy:An Empirical Study of the Effectiveness of the Balanced Score‐card[J].Journal of Management Accounting Research,2001(13):47‐90.
[66]Neely,A.,Adams,C. & Kennerley,M.The Per formance Prim‐the Scorecard for Measuring and Managing Business success[M].FT Prentice Hall,London,2002.
[67]Vikram Mahidhar and Christine Cutten,Navigating the Market‐ing Measurement Maze[J].Journal of Integrated Marketing Communi‐cations,2007.
[68]Phillips,B. & Shanka,T.Balanced Scorecard(BSC)Measures in Small and Medium Enterprises(SMEs)‐An Exploratory Study,in R.Shaw,S.Adam & H.McDonald(eds.)[J].Proceedings of the Australian and New Zealand Marketing Academy Conference(A NZMAC),2002:2451‐2456.
[69]Piercy Nigel,Morgan Neil.Customer satisfaction measurement and management:A processual analysis[J].Journal of Marketing Management,1995(11):817‐834.
[70]Ricks D.Chain management and marketing performance in fruit industry[J].Alta Horticultures,2000(536):66‐668.
[71]Rust R.T.,Ambler,T.,Carpenter G.S.,Kumar,V.,Sriv‐astava R.K.Measuring marketing productivity:Current knowledge and future directions[J].Journal of Marketing,2004(68):76‐89.
[72]Sevin,Charles H.Marketing Productivity Analysis[M].Mcgraw‐Hill,New York,1965:246‐357.
[73]Sheth J.N.,Sisodia R.S.Feeling the Heat[J].Marketing Management,1995(4):8‐23.
[74]Sheth,J.N., & Sisodia,R.S.Marketing productivity issues and analysis[J].Journal of Business Research,2002,55(5):349‐362.
[75]Simon Carol J.,Sullivan,Mary W.The measurement and deter‐minations of brand equity:a financial approach[J].Marketing Science,1993,12(1):28‐52.
[76]Tallman,S.B.Strategic management models and resource based strategies among MNEs in a host market[J].Strategic Manage‐ment Journal,1991(12):69‐82.
[77]Tai‐Ching Chiang.The Empirical Study of Applying Data Mining to Escalate Marketing Performance,International Conference on Cyber‐netics and Information Technologies[J].Systems and A pplications(CIT‐SA2004)and International Conference on Information Systems Analysis and Synthesis,Orlando,FL(US),2004(1):239‐244.
[78]Walker Orville C.,Ruekert Robert W..Marketing's role in theImplementation of business strategies:a critical review and conceptual framework[J].Journal of Marketing,1987,51(3):15‐33.
[79]Wind Y.,Mahajan V.,Swire,D.J.An empirical comparison of standardized portfolio models[J].Journal of Marketing,1983(47):89‐99.
[80]Wyner Gordon.Scorecards and More[J].Marketing Research,2003(15):63‐68.
[81]Yi,Youjae.A Critical Review of Customer Satisf action[M],A.Zeithaml,Ed.Review of Marketing,American Marketing Association,Chicago,1990:68‐123.
[82]ZhaoH.,Luo,Y.Productdiversification,ownership structure,and subsidiary performance in China's dynamic market[J].Management International Review,2002(42):27‐48.
免责声明:以上内容源自网络,版权归原作者所有,如有侵犯您的原创版权请告知,我们将尽快删除相关内容。















